The Labour Appeal Court (LAC) has handed down a compelling decision that tackles a question many employers and legal practitioners grapple with:
can a disciplinary chairperson reject a lenient sanction that emerges from a plea‑bargaining process? The response to this question was provided by the LAC in
South African Police Services v Mkonto and Others.1 We unpack this important case in detail below.
Mr Mkonto was a sergeant in the South African Police Service (SAPS). He was charged with serious misconduct for the unauthorised use and parking of a SAPS vehicle. During the disciplinary hearing, he pleaded not guilty. SAPS led evidence from its first witness before the matter was postponed due to the second witness being unavailable.
Mr Mkonto and SAPS entered into a plea‑bargaining agreement where he would change his plea to guilty in exchange for a lenient sanction. The chairperson was informed of the agreement and accepted the revised plea. However, given the seriousness of the misconduct, the chairperson rejected the proposed lenient sanction and instead imposed a dismissal.

The LAC first held that the plea‑bargaining agreement was not binding on the disciplinary chairperson. This is because the SAPS Disciplinary Regulations require the chairperson to independently determine an appropriate sanction after considering all mitigating and aggravating factors.
The LAC then considered the procedure the chairperson should have followed. It warned that chairpersons cannot selectively accept only the parts of a plea‑bargaining agreement that appeal to them. Instead, the court set out a clear four‑pronged set of guidelines to be followed whenever such agreements are placed before a chairperson.
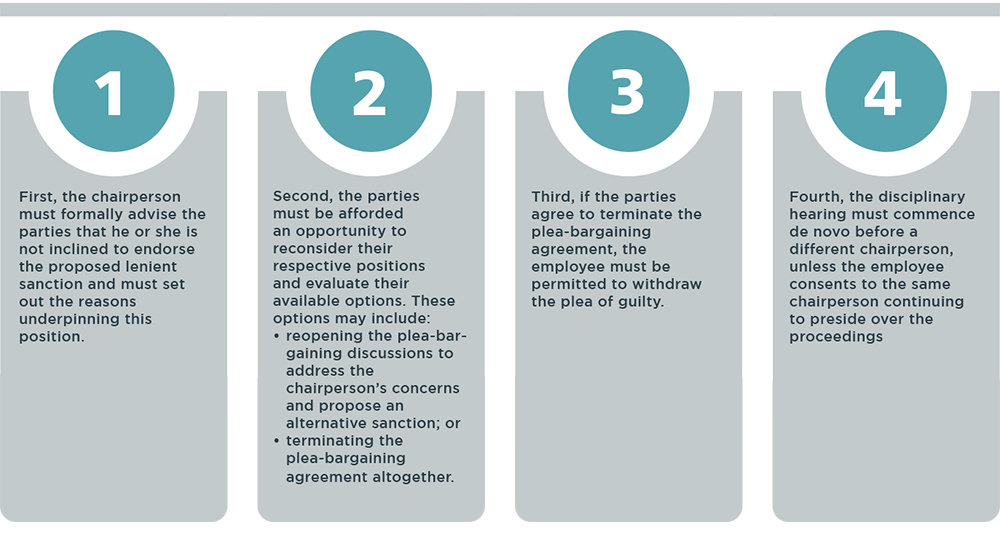
The court emphasised that these guidelines are not peremptory; their application will depend on the specific facts of each case.
Key takeaways from the judgment
Plea bargains in labour matters constitute a useful mechanism to resolve disciplinary issues in an expedient manner resulting in the charged employee, initiator and witness to focus on revenue generating activities rather than being involved in protracted disciplinary hearings. This is in accordance with item 2(2) of the Code of Good Practice: Dismissal.
Employers should ensure that their disciplinary policies include plea-bargain agreements, the principle that the chairperson is not bound by a plea-bargain agreement, and the process to be followed where the chairperson rejects the plea-bargain agreement in whole or in part. Employers should also include a full and final settlement clause in the plea-bargain agreement to avoid employees challenging the sanction imposed at a later stage.
1 -
South African Police Services v Mkonto and Others 2026 ZALAC